What is a spa pool heat pump?
A pool heat pump is a heating system designed to warm pool water by extracting heat from the surrounding environment. It operates by utilizing a compressor and refrigerant to extract heat from ambient air and transfer it into the pool water.
A spa heat pump is a specialized heating system designed for warming spas or hot tubs. They operate similarly to pool heat pumps but are optimized for smaller water volumes.

Does a spa pool heat pump can save you money?
While a heat pump system is relatively energy-efficient, whether it saves you money depends on various factors.
Pros
- High Efficiency: Spa heat pumps use ambient heat to warm water, consuming less energy compared to traditional resistance heating, which can result in cost savings.
- Long-Term Savings: While initial installation costs may be high, the savings over time become apparent as the system operates.
Cons
- Higher Initial Investment: Initial installation costs for a spa heat pump might be higher compared to other heating methods, such as resistance heating.
- Maintenance Costs: Regular maintenance and cleaning may increase maintenance costs at times.
Other Aspects
- Reliability: Spa heat pumps are generally reliable, providing consistent heating over time.
- Temperature Control: These pumps offer precise temperature control, allowing users to set the desired water temperature.
- Applicability: Suitable for various sizes of spas and hot tubs, providing heating that matches the equipment capacity.
- Long-Term Savings: Despite the high initial investment, the lower energy consumption over time makes it cost-effective.
In summary, spa heat pumps tend to be energy-efficient, especially for long-term usage that results in energy cost savings. However, consideration must be given to their initial investment and regular maintenance costs. Whether a spa heat pump saves you money depends on your specific usage patterns and long-term plans.
How a spa pool heat pump works?
A spa pool heat pump operates on a principle similar to that of an air conditioner but in reverse. Instead of generating heat, it extracts heat from the surrounding air and transfers it to the water in the spa pool.
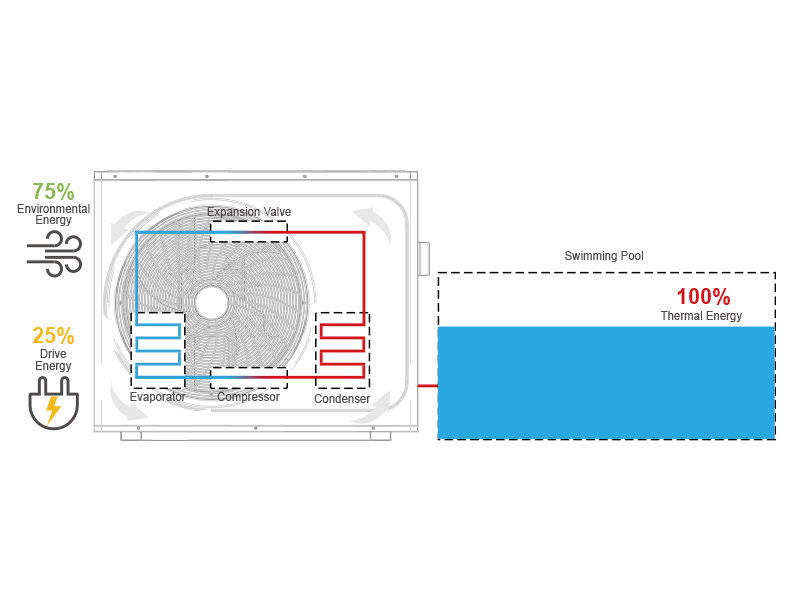
Here’s a simplified overview of how it works:
- Absorption of Warmth: The heat pump draws in air from the surroundings using a fan. Even in colder climates, there’s latent heat available in the air, which the heat pump captures.
- Vapor Compression Cycle: Inside the heat pump, the captured air passes through an evaporator coil. A refrigerant, often in a gaseous state, circulates through this coil. As the air passes over the coil, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the air, causing it to evaporate and turn into a gas.
- Compression and Heating: The compressor in the heat pump compresses this gas, increasing its temperature. This high-temperature, high-pressure gas then moves to the condenser coil.
- Heat Transfer: In the condenser coil, the hot gas releases its heat to the cooler water from the spa pool. As the gas loses heat, it condenses back into a liquid state.
- Repeat Cycle: The liquid refrigerant then passes through an expansion valve or capillary tube, which reduces its pressure. This process readies the refrigerant to absorb more heat in the evaporator, and the cycle begins again.
By continuously cycling through this process, the heat pump transfers heat from the surrounding air to the water in the spa pool, effectively raising the water temperature.
Factors like the efficiency of the heat pump, the ambient temperature, and the desired water temperature affect how efficiently and quickly this process can heat the water in the spa pool. Heat pumps are known for being more energy-efficient compared to traditional electric or gas heaters, as they move heat rather than generating it, making them a popular choice for heating pools and spas.
What size heat pump do I need for my spa pool?
Determining the right size heat pump for your spa pool involves considering a few key factors:
- Pool Volume: Calculate the volume of your spa pool. This can be done by multiplying the length, width, and average depth of the pool. The formula for a rectangular pool is length × width × average depth. For irregular shapes, you may need more complex calculations or consult a pool professional.
- Temperature Requirements: Determine the desired temperature increase for your spa pool. For instance, if you want to maintain a temperature of 100°F (37.8°C) and your average ambient temperature is 50°F (10°C), you’ll need to raise the temperature by 50°F.
- Heat Pump Efficiency: Consider the efficiency rating (COP or coefficient of performance) of the heat pump you’re considering. This rating indicates how efficiently the heat pump can heat the water. Higher COP values indicate better efficiency.
- Climate: Your local climate also plays a role. Colder climates might require larger heat pumps or additional heating sources to maintain desired temperatures efficiently.
Once you have this information, you can use it to estimate the size of the heat pump you need. Generally, a rough guide is to look for a heat pump with an output that matches or slightly exceeds the calculated heat loss of the pool.
However, it’s highly recommended to consult with a pool professional or a heat pump specialist. They can perform detailed heat loss calculations based on your specific spa pool, climate conditions, and other relevant factors to accurately determine the appropriate size of the heat pump for your needs. This helps ensure efficient heating without overspending on a larger unit or struggling with an undersized one.
How to install a spa pool heat pump?

Installing a heat pump for a spa pool or swim spa typically involves several steps to ensure proper functioning and safety:
- Select the Right Heat Pump: Choose a heat pump that’s suitable for the size of your spa or swim spa. Consider factors like the volume of water to be heated and the climate in your area.
- Location: Find an appropriate location for the heat pump. It should have enough space around it for proper airflow and maintenance access. Ensure it’s close enough to the spa or swim spa for plumbing connections.
- Plumbing Connections: Connect the heat pump to the spa’s plumbing system. This usually involves attaching the intake and return pipes to the heat pump. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for proper sizing and connection.
- Electrical Connection: Ensure the heat pump is connected to a suitable power source according to the manufacturer’s specifications. This might involve hiring a qualified electrician to handle the electrical connections.
- Positioning and Mounting: Mount the heat pump securely on a level surface. Make sure it’s properly aligned and positioned according to the manufacturer’s guidelines to avoid vibration and ensure optimal performance.
- Airflow: Ensure there’s adequate airflow around the heat pump. Trim back any vegetation or obstacles that might obstruct airflow to the unit.
- Testing and Commissioning: Once the installation is complete, test the heat pump to ensure it’s functioning correctly. Check for leaks, verify the temperature settings, and make any necessary adjustments.
- Regular Maintenance: Follow the maintenance schedule outlined in the heat pump’s manual. This might include cleaning the filters, inspecting the unit, and scheduling professional servicing at recommended intervals.
It’s crucial to refer to the specific installation instructions provided by the manufacturer of the heat pump as different models may have variations in installation procedures. If you’re unsure about any step or aspect of the installation process, consider consulting a professional or hiring a certified technician to ensure the heat pump is installed correctly and safely. Safety should always be a priority when working with electrical and plumbing systems.
What distance from my pool should I install a heat pump?
For optimal performance, it’s recommended to install a heat pump as close to the pool’s filter as possible and around 25 feet away from the swimming pool itself. Placing the unit farther from the pool could result in heat loss due to the underground tubing. This distance allows efficient heating without sacrificing effectiveness due to excessive tubing length.
The installation of an air source swimming pool heat pump water heater demands meticulous attention and professional handling. Careful adherence to guidelines and best practices ensures not only the equipment’s performance and lifespan but also the safety and comfort of users. Thoroughly research the guidelines and requirements before installation and consistently apply best practices.
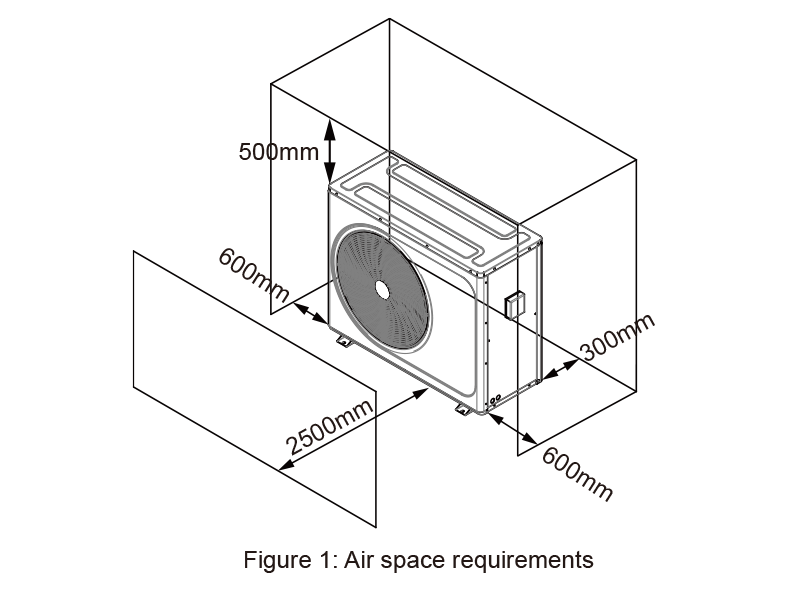
Can I install a pool heat pump myself?
Installing a pool heat pump can be a complex task that requires knowledge of electrical systems, plumbing, and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) principles. It involves handling electrical connections, piping, and ensuring proper setup for efficient operation. Due to the technicalities involved, it’s often recommended to have a professional handle the installation.
However, if you have experience and knowledge in these areas, along with a good understanding of the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for installation, it’s possible to install a pool heat pump yourself. Here are some considerations:
Considerations for DIY Installation:

- Manufacturer’s Instructions: Thoroughly review and understand the installation manual provided by the manufacturer. Follow each step meticulously to ensure proper setup.
- Skills and Experience: Assess your proficiency in handling electrical connections, plumbing, and HVAC systems. If you lack experience in any of these areas, it might be safer to hire a professional.
- Local Regulations and Codes: Ensure compliance with local regulations and codes governing electrical and pool installations. Failure to adhere to these could pose safety risks and might invalidate warranties.
- Safety Precautions: Prioritize safety during the installation process. Pool heat pumps involve electrical connections and handling refrigerants, which can be hazardous if mishandled.
- Tools and Equipment: Make sure you have the necessary tools and equipment required for installation. This includes tools for plumbing, electrical work, and testing.
- Warranty Concerns: Check the manufacturer’s warranty terms. Some warranties might require professional installation to remain valid.
- Seeking Professional Assistance: If you encounter any uncertainties during the installation process, it’s better to seek professional assistance rather than risking improper installation.
Final Note:
While DIY installation might be feasible for individuals with the right skills and experience, it’s crucial to prioritize safety and compliance with regulations. If in doubt or if the process seems too complex, consulting or hiring a professional installer is a wise choice to ensure a safe and efficient installation of your pool heat pump.
Finnaly, here is an ‘Air Source Swimming Pool Heat Pump Water Heater Installation Guide‘ for you:
- Selecting the Suitable Location
- Space Requirements: Ensure adequate space is available to accommodate the heat pump water heater while maintaining proper ventilation around it.
- Noise Avoidance: Consider placing the heat pump away from main activity areas to minimize noise disturbance.
When choosing a location, consider both the physical space needed for the heat pump and its distance from areas where noise might be an issue. It’s essential to maintain a balance between accessibility and minimizing disruptions.
- Pre-Installation Preparation
- Power Supply Requirements: Confirm an adequate power supply and adhere to the electrical specifications provided by the manufacturer during installation.
- Pipe Connections: Prepare pipes of the appropriate size and material, ensuring connections adhere to recommended standards.
Before initiating the installation process, ensure that all electrical requirements are met and that you have the necessary piping and connections ready.
- Installation Process
- Secure Installation: Utilize appropriate supports and mounting fixtures to securely install the heat pump on the ground or a wall.
- Pipe Connections: Ensure a secure connection of pipes to prevent leaks, following the instruction manual for proper inlet and outlet pipe connections.
- Electrical Connection: Follow the manufacturer’s provided electrical schematics to correctly connect the power supply, ensuring proper and secure wiring.
During the installation process, attention to detail is crucial to ensure all connections are secure and in accordance with the provided guidelines.
- Debugging and Testing
- System Check: Prior to starting the system, inspect all connections and fittings to ensure no loose or damaged parts.
- Pressure Testing: Conduct pressure tests to verify that the piping system and connections are leak-free.
- Electrical System Check: Inspect the electrical system to ensure all connections are correct and comply with safety standards.
Conducting thorough checks and tests before the system starts operating is critical to identify and rectify any potential issues.
- Start-Up and Adjustment
- System Start-Up: Initiate the heat pump system and perform initial settings and adjustments as per the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Performance Testing: Conduct tests to evaluate the heat pump water heater’s performance, including heating speed, temperature control, and energy efficiency.
After the system is operational, it’s essential to test its performance to ensure it meets expected standards and operates efficiently.
- Documentation and Maintenance
- Data Recording: Record initial performance data and relevant parameters for future reference and comparison.
- Maintenance Schedule: Develop a regular maintenance schedule, including tasks like filter cleaning, pipe inspections, and electrical system checks.
Maintaining detailed records and implementing a regular maintenance plan is crucial for the continued optimal performance and longevity of the heat pump water heater.
Key Considerations
- Adherence to Manufacturer Guidelines: Strictly follow the installation manual and guidelines provided by the manufacturer to ensure compliance with requirements.
- Prioritize Safety: Adhere strictly to safety regulations and standards throughout the installation process to ensure the safety of installers and users.
- Professional Qualifications: It is recommended to have installation and debugging performed by professionals with relevant qualifications and experience.
One step towards carbon neutrality: Fossil Fuel vs Heat Pump
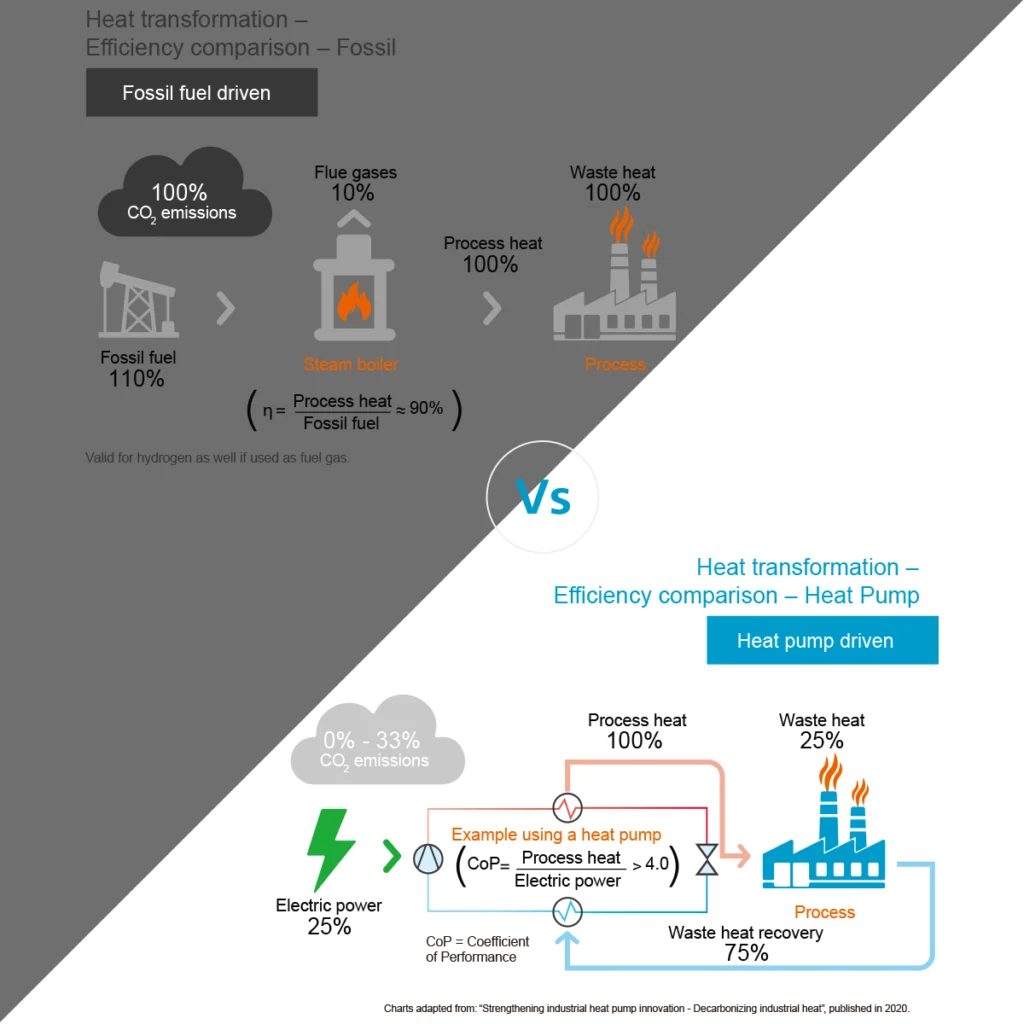
Moving toward carbon neutrality often involves transitioning away from fossil fuels toward more sustainable alternatives like heat pumps.
Fossil Fuels:
- Usage: Fossil fuels like natural gas or propane are commonly used to heat pools or homes. They produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and other pollutants when burned, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Carbon Footprint: Burning fossil fuels releases CO2 into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change. The carbon footprint associated with fossil fuels is substantial.
- Efficiency: While fossil fuel systems can be efficient in heating, their overall efficiency is lower compared to heat pumps. They rely on combustion, which inherently loses energy as heat, impacting their efficiency.
Heat Pumps:
- Usage: Heat pumps work by transferring heat rather than generating it, making them highly efficient. They use electricity to move heat from one place to another, making them a more sustainable option.
- Carbon Footprint: Heat pumps, particularly those powered by renewable energy sources like solar or wind power, can significantly reduce carbon emissions. They produce fewer emissions directly and can operate with zero emissions if powered by renewable electricity.
- Efficiency: Heat pumps are highly efficient, especially in moderate climates. They can extract heat from the air, ground, or water and amplify it, providing efficient heating without burning fossil fuels.
Transitioning from fossil fuel-based heating systems to heat pumps aligns with carbon neutrality goals by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. However, the overall impact depends on various factors, including the energy source used to power the heat pump.
For a genuine step toward carbon neutrality, pairing heat pumps with renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power maximizes their potential in reducing carbon emissions. This combination significantly minimizes the environmental impact associated with heating pools or homes, making it a crucial step in achieving carbon neutrality.




