Table of Contents
What is a Heat Pump?
The heat pump system, as a part of home heating and cooling, not only cools the home but also provides heating. They use refrigerants to transfer heat from indoor to outdoor spaces, and in warmer months, they extract heat from indoor air. These systems, installed outside your house and powered by electricity, maintain comfortable indoor temperatures throughout the year without the need for additional heating systems.

What are the types of heat pumps?
There are 3 types of Heat Pumps:
1.Air Source Heat Pumps (ASHP):
- ASHPs extract heat from the outdoor air and use it for heating purposes indoors. They work by absorbing heat from the ambient air and transferring it indoors through a refrigerant cycle.
- They are commonly used in moderate climates where temperatures don’t typically drop extremely low. ASHPs are efficient and cost-effective for both heating and cooling purposes.
There is another term “ATW heat pump”, which stands for “Air-to-Water heat pump.” It’s the most common type of heat pump that extracts heat from the outdoor air and transfers it to water, typically for heating indoor spaces or for domestic hot water usage.
An ATW heat pump operates similarly to an air source heat pump (ASHP), which draws heat from the outside air. However, the key difference lies in how the extracted heat is utilized. While an ASHP might directly distribute the heat into the indoor air, an ATW heat pump transfers the gathered heat to a water-based system.
This type of heat pump is commonly used in hydronic heating systems where water is circulated through underfloor heating systems, radiators, or used for domestic hot water purposes. The heat extracted from the outdoor air is transferred to the water, which is then circulated through the building to provide warmth.
ATW heat pumps are known for their efficiency and versatility, offering both heating and potentially cooling capabilities by utilizing the latent heat present in the ambient air. They are particularly popular in moderate climates where they can efficiently extract heat from the air even in lower temperatures.
2.Water Source Heat Pumps (WSHP):
- WSHPs operate similarly to GSHPs but extract heat from a water source such as a well, lake, or river instead of the ground.
- They use water as the heat exchange medium to transfer heat into a building or to provide heating or cooling.
- WSHPs are advantageous in areas where water sources are available and can provide consistent and efficient heating and cooling.
3.Ground Source Heat Pumps (GSHP or Geothermal Heat Pumps):
- GSHPs harness heat from the ground or a body of water, using a ground loop system buried underground or submerged in water.
- They are highly efficient because underground temperatures are relatively stable throughout the year, providing consistent heating or cooling regardless of external weather conditions.
- GSHPs require more initial installation costs due to the ground loop system but offer long-term energy savings.
Each type of heat pump has its advantages and is suitable for different environmental conditions and geographical locations, catering to various heating and cooling needs.
In addition, according to the design and system composition of the heat pump, it can also be divided into Split heat pump and Monobloc heat pump. While a monobloc heat pump consolidates most components into a single unit, a split heat pump separates key components into indoor and outdoor units connected by refrigerant lines.
Split Heat Pump:
- Design Features: A split heat pump comprises two separate units—an indoor unit and an outdoor unit. The outdoor unit contains the compressor and condenser, while the indoor unit houses the evaporator and expansion valve.
- Characteristics: A split heat pump connects the indoor and outdoor units through refrigerant lines. This design requires more installation steps and space, potentially involves more complex maintenance but offers flexibility to adapt to various installation requirements.
Monobloc Heat Pump:
- Design Features: A monobloc heat pump integrates most essential components within a single outdoor unit, typically including the compressor, heat exchangers (evaporator and condenser), expansion valve, and control system.
- Characteristics: The design of a monobloc heat pump is simple, installation and maintenance are relatively straightforward, it offers a tidy appearance, and generally has a more compact structure.
What are the key components of a Heat Pump System?
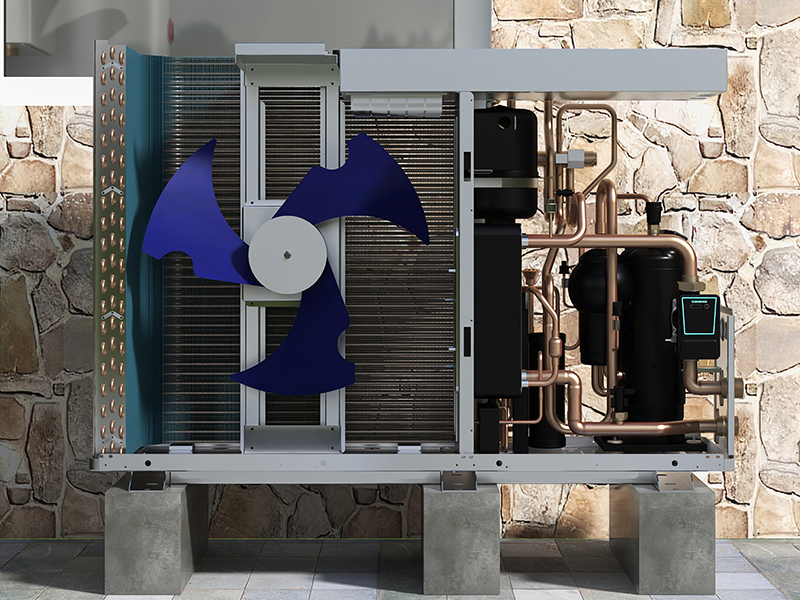

- Compressor: This is the heart of the heat pump system. The compressor pressurizes and circulates the refrigerant, facilitating the heat exchange process. In a monobloc heat pump, the compressor is integrated into the outdoor unit, usually in a compact and enclosed design.
- Heat Exchanger (Condenser and Evaporator Coils): Monobloc heat pumps contain heat exchanger coils for both the condensation and evaporation of the refrigerant. The condenser coil releases heat to the indoor environment during heating mode and absorbs heat from indoors during cooling mode. The evaporator coil absorbs heat from the outdoor air or ground during heating mode and releases it into the refrigerant.
- Expansion Valve: This component regulates the flow of refrigerant, controlling its pressure and temperature. It allows the refrigerant to expand from a high-pressure liquid to a low-pressure liquid-gas mix before entering the evaporator coil to absorb heat from the external environment.
- Controller and Electronics: The control unit and electronics in a monobloc heat pump manage the system’s operation. It monitors and regulates the temperature, activates various components like the compressor and fans, and may include smart features for efficiency optimization and system monitoring.
These components work together to facilitate the heat exchange process, enabling the heat pump to extract heat from the external environment (air, ground, or water) and transfer it to the indoor space for heating or remove heat from indoors for cooling purposes. The monobloc design streamlines installation and maintenance since most of the vital components are housed in a single outdoor unit.
How does a heat pump works?
Air source heat pumps are revolutionary devices designed to efficiently transfer heat from the ambient air to provide heating and hot water for residential and commercial spaces. They operate on a principle similar to that of a refrigerator but in reverse.
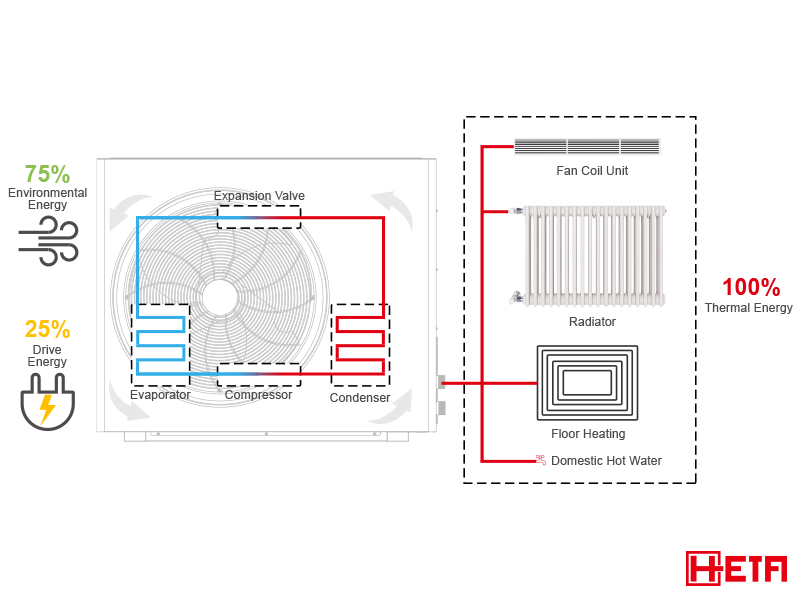
- Heat Absorption:
The process begins with the heat pump’s refrigerant fluid, typically a compound like R32, which circulates within the system. When the pump is in heating mode, the refrigerant passes through an evaporator coil, absorbing thermal energy from the outdoor air even in cold temperatures as low as -25°C. - Compression and Temperature Increase:
The absorbed heat causes the refrigerant to evaporate into a gas. This low-temperature gas is then compressed by the compressor within the heat pump, significantly raising its temperature. This process turns the gas into a high-pressure, high-temperature state. - Heat Release:
The now hot refrigerant gas passes through a condenser coil, where it releases its accumulated heat to the indoor space or to heat water. This heat is then distributed throughout the building via a fan system or used to warm up the water in a tank for domestic purposes. - Repeating the Cycle:
After releasing its heat, the refrigerant returns to a liquid state and flows back to the evaporator to begin the cycle again. This continuous process of absorbing heat, compressing the refrigerant, releasing heat, and then returning to the starting point constitutes the operational cycle of an air source heat pump.
Operating Principles of Heat Pumps
In the cooling mode, heat pumps absorb indoor heat and release it outdoors.
In the heating mode, they absorb heat from the ground or outdoor air and release it indoors.
These advanced heat pump systems are not constrained by environmental temperatures and maintain stable operations even in extreme conditions.
What are the advantages of a Heat Pump?
- Efficiency: Air source heat pumps can provide efficient heating and hot water even in colder climates, though their effectiveness may decrease as temperatures drop.
- Environmental Impact: They use the heat from the air, which is a renewable resource, making them environmentally friendly compared to traditional heating systems reliant on fossil fuels.
- Versatility: Air source heat pumps can also work in reverse during warmer months, acting as air conditioners by removing heat from indoor spaces and transferring it outside.
Future Trends in Heat Pumps
Cutting-edge technology makes heat pump systems more eco-friendly and efficient. As technology advances, future heat pump systems will be more intelligent, efficient, and environmentally friendly.
In recent years, heat pump water heaters have surged in popularity as efficient and eco-friendly hot water solutions. Some ATW heat pumps are able to operates at a temperature range from -25°C to 43°C.

The evolution of these heat pumps, such as Hetapro Thermalux R290 ATW Heat Pump, has elevated technology to unprecedented levels. Equipped with R290 refrigerants, DC inverter compressors, and Enhanced Vapor Injection (EVI) technology, these latest heat pumps can achieve impressive temperatures of up to 75°C. Remarkably, they maintain steady operation even in extreme conditions, enduring temperatures as low as -35°C.
Conclusion
Air source heat pumps utilize a smart and eco-friendly mechanism to harness latent heat from the air, offering an efficient solution for heating and hot water needs in various settings.
The evolving heat pump systems have become an ideal choice for home heating, cooling, and hot water supply. The latest heat pump water heaters using R290 refrigerants not only offer high efficiency but also set an example for the development of eco-friendly technology.




